Cholesterol is a soft, fat-like, waxy substance found only in animal products. Too much cholesterol can lead to a buildup of fatty materials and debris, called plaque, on the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart and other organs. The body needs some cholesterol for normal body functions, as it plays a role in forming cell walls, producing hormones, and manufacturing bile acids essential for digestion. Since our liver can make all the cholesterol our bodies may require, there is no need to consume extra cholesterol in our diets. Elevated levels of bad cholesterol can lead to chronic and debilitating health conditions like heart disease and stroke.
You May Also Like:
Support Your Heart Health: Comparing 2 Top Supplements
5 Great Ways Liquid Protein Supplements Can Take Your Fitness to the Next Level
How to Lower Cholesterol Levels Fast: The Secret of Phospholipids is an original (OptimalHealthNews) article.
Understanding how to lower cholesterol levels with HDL
Cholesterol can be broadly categorized into low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, and high-density lipoprotein, known as HDL. Higher LDL levels are linked to a higher risk of heart disease. LDL causes plaque buildup in your blood vessels, which makes them hard and narrow. This, in turn, reduces or even blocks the flow of blood and oxygen that your heart needs, potentially leading to chest pains, heart attacks, or stroke.
On the other hand, HDL is considered “good” cholesterol because it helps move excess cholesterol out of the arteries. It circulates through your body like a vacuum cleaner, sucking out cholesterol from the blood vessels. HDL acts as a scavenger, removing excess cholesterol from tissues and transporting it to the liver to be excreted.
When you come across discussions about high and low cholesterol, such as high-cholesterol foods or ways to lower your cholesterol levels, it almost always refers to LDL or bad cholesterol. To keep your body at its best, you should aim to have high levels of HDL and low levels of LDL. You want to have high enough levels of good cholesterol to combat the negative effects of bad cholesterol effectively.
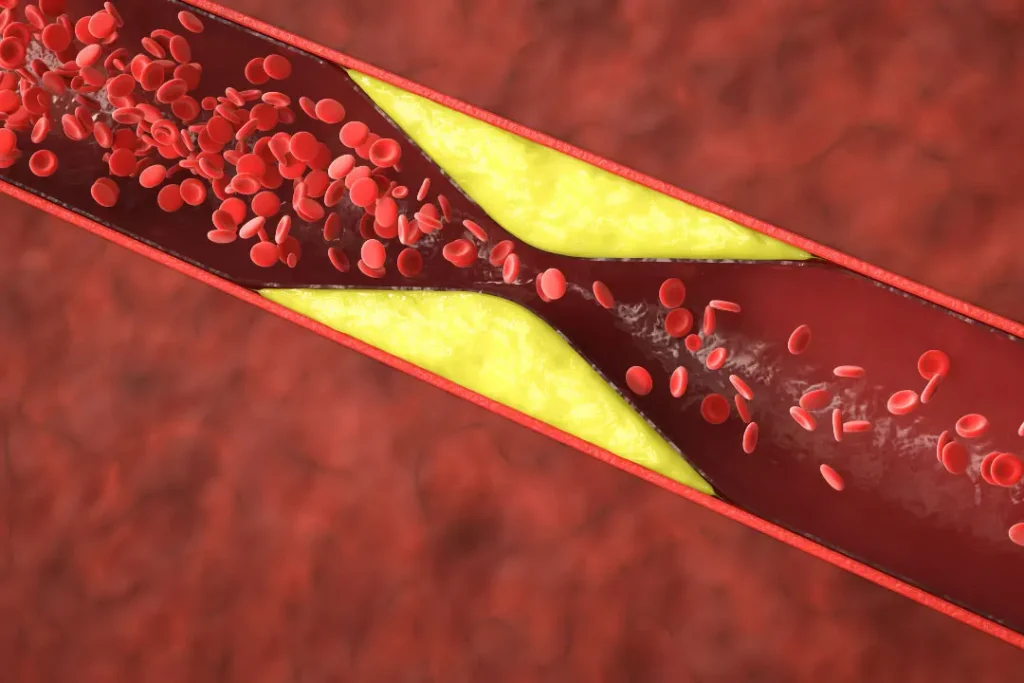
How to lower cholesterol levels with phospholipids
Phospholipids are gaining a lot of attention for their potential to lower cholesterol levels quickly and effectively. In this article, we will explore in more detail how phospholipids can be used to swiftly decrease levels of bad cholesterol.
Phospholipids play many vital roles in our health and are involved in various biological processes. For example, within krill oil, most of the EPA and DHA omega-3s are bound to phospholipids. These molecules are a crucial component of cell membranes, which function to separate the interior of cells from the outside environment and provide vital structural support.
Phospholipids have shown promise in managing cholesterol levels because they can interact with cholesterol molecules. This interaction facilitates the transportation and excretion of cholesterol from the body. As a result, phospholipids play a vital role in lowering levels of LDL, or bad cholesterol. This mechanism helps reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
How to lower cholesterol levels:
Phospholipid benefits
Enhanced lipid metabolism: Phospholipids play a role in lipid metabolism, including cholesterol. By aiding in the transport of cholesterol, they contribute to overall lipid balance.
Reduced LDL oxidation: Phospholipids possess antioxidant properties that can prevent LDL oxidation. This is crucial in preventing the formation of artery-clogging plaques. Higher levels of phospholipids within LDL can potentially reduce its susceptibility to oxidation. Oxidation can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, commonly known as the hardening of the arteries.
Cell membrane health: Healthy cell membranes are essential for proper cholesterol regulation. Phospholipids help maintain the integrity of the cell membrane, thus ensuring the proper functionality of cells engaged in cholesterol metabolism.
Liver health: Phospholipids help support liver function. The liver is a vital organ involved in cholesterol synthesis and metabolism.
Anti-inflammatory effects: Certain phospholipids exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation contributes to hardening of the arteries. By reducing inflammation, phospholipids may indirectly support healthier cholesterol levels.

How to lower cholesterol levels with lifestyle changes
Balanced diet: If you want to maintain healthy levels of cholesterol, it’s recommended that you consume foods that are rich in natural phospholipids, such as meat, eggs, soybeans, sunflower seeds, seed oils, and seafood. Phospholipid-rich seafood includes fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and herring. Phospholipids are also found in some plant foods but in much smaller amounts.
Most American diets are lacking in omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA and EPA. Many Americans simply don’t consume enough seafood. Western diets often consist of processed foods and vegetable oils. Seafood sources of phospholipids show more potential in helping to manage cholesterol levels, but the difficulty is in convincing Americans that they should be eating more seafood.
Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a regular routine of physical activity and managing stress levels can complement the effects of phospholipids in reducing levels of bad cholesterol.
Hydration: Adequate hydration supports lipid metabolism and overall cardiovascular health.
Monitor cholesterol levels: Regular cholesterol level checks will help track the effectiveness of dietary changes involving phospholipids.
How to lower cholesterol levels with supplementation
If adhering to a balanced diet is too inconvenient, you might want to try phospholipid-rich omega-3 supplements. Notably, seafood sources of phospholipids are much better than plant sources. The best marine source is krill, a small ocean crustacean. Krill boasts a remarkable 40% phospholipid content, whereas other seafood sources contain about 1%. Furthermore, it has also been suggested that omega-3 fats from krill are more bioavailable than omega-3s from fish oil. This heightened bioavailability is because the majority of DHA and EPA in krill oil is bound to phospholipids, which the body absorbs effectively.
Several studies have explored the effects of phospholipids on cholesterol levels. One randomized clinical trial showed that phospholipid supplementation led to improvements in lipid profiles, including increased HDL levels. It’s important to note that individual responses to phospholipid interventions may vary. Genetic factors, underlying health conditions, and overall dietary patterns can influence the results. With a plethora of supplements available, our attention will now shift to one of the best phospholipid supplements on the market.

Kori Krill Oil’s Mind & Body Omega-3:
A premier source of phospholipid supplements
Kori Krill Oil’s Mind & Body Omega-3 stands out as an exceptional phospholipid supplement. This potent formulation is packed with krill oil omega-3s, antioxidants, B12, and turmeric curcumin. Compared to traditional fish oil, Kori Krill Oil offers superior omega-3 absorption. It achieves this by providing omega-3s in their most natural phospholipid form, just as you would find in a healthy fish-based diet. Phospholipids enable better omega-3 absorption and easier digestion. Fish oil tends to lose its absorption and digestion capabilities during processing. The presence of phospholipids in Kori Krill Oil contributes to improved ease of digestion, ensuring the absence of any fishy aftertaste.
Each daily serving of this supplement provides 250mg of omega-3 EPA and DHA, the same amount you would receive from consuming two recommended servings of fish per week.
How to lower cholesterol levels:
The next steps
Phospholipids offer a promising approach to rapidly lower cholesterol levels due to their role in cholesterol metabolism, antioxidant properties, and support for overall cardiovascular health. In addition, their roles in cholesterol transportation, lipoprotein stability, and various metabolic pathways make them valuable interventions. While dietary sources of phospholipids can be included in a heart-healthy diet, supplementation with krill oil may provide concentrated benefits.
However, it’s important to remember that phospholipids are just one part of a comprehensive strategy. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and consultation with a healthcare professional stand as crucial elements for achieving and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. As ongoing research reveals more information about the complex interactions between phospholipids and cholesterol metabolism, you may want to consider these strategies as part of a comprehensive approach to managing cholesterol levels and reducing your risk for heart disease.

For further reading:
Harvard Health: Beyond bad cholesterol, a closer look at your blood lipids
Men’s Health: 8 ways to increase HDL cholesterol
CNN: Reduce cholesterol earlier in life to prevent heart problems later
Forbes: Cholesterol levels: Normal ranges by age LDL HDL and more
Good Housekeeping: The best foods that can lower your cholesterol naturally
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
